Lymphedema is a chronic health condition caused by the accumulation of lymph fluid in the tissues, most commonly in the arms or legs, but it can affect other parts of the body as well. This disease results from lymphatic system dysfunction, which is crucial for maintaining fluid balance and immune defense. Lymphedema can significantly impact the quality of life, but timely diagnosis and appropriate therapy can alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
Causes and Types of Lymphedema
Lymphedema can be primary or secondary, depending on its underlying cause.
- Primary lymphedema is a rare, inherited condition caused by congenital lymphatic system disorders. It can develop at any age, but the first symptoms often appear during adolescence or early adulthood. It is caused by abnormal development of the lymphatic vessels or nodes, leading to reduced lymph fluid flow and accumulation in the tissues.
- Secondary lymphedema is much more common and occurs due to damage to the lymphatic system. The most common causes include surgical procedures, radiation, injuries, infections, or inflammatory conditions leading to lymphatic vessel blockages. Individuals who have undergone cancer treatment, especially for breast cancer, gynecological tumors, or melanoma, are at an increased risk of developing lymphedema, particularly if lymph nodes were removed or if they underwent radiation therapy.
Regardless of the cause, lymphedema requires constant attention and appropriate therapy to prevent the worsening of symptoms and the development of complications.
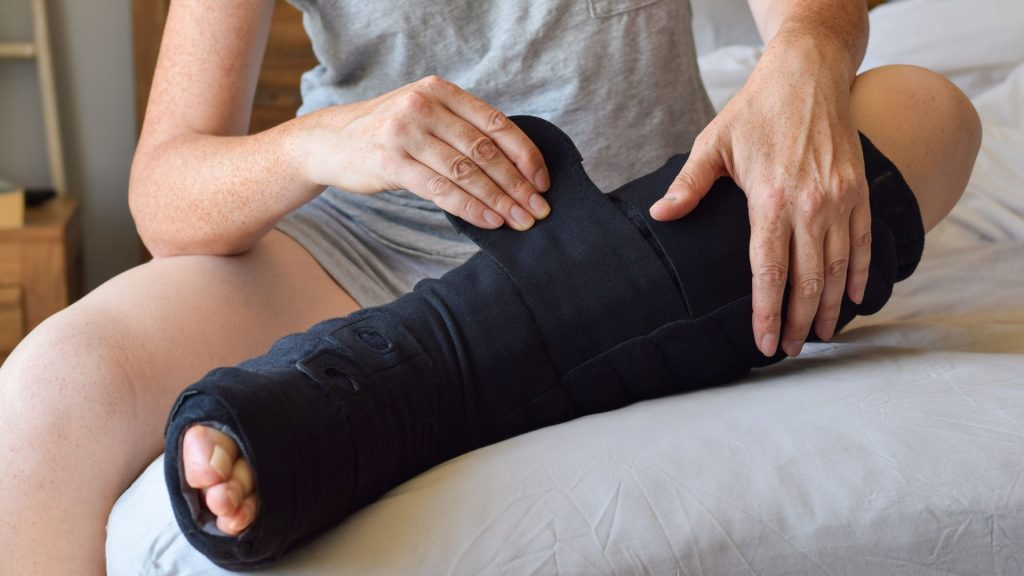
Symptoms and Treatment Options
Lymphedema is most commonly recognized by swelling in the affected part of the body, which can range from mild to pronounced. In addition to swelling, people with lymphedema often experience:
- Heaviness and tightness in the affected area
- Pain and discomfort, especially when standing or sitting for long periods
- Thickening and tightness of the skin, which may lead to limited mobility
- An increased risk of infections, such as cellulitis, due to reduced circulation and weakened immune function
The treatment of lymphedema focuses on controlling symptoms and preventing complications. Currently, no cure can completely resolve lymphedema, but there are effective therapeutic methods that help maintain an everyday life:
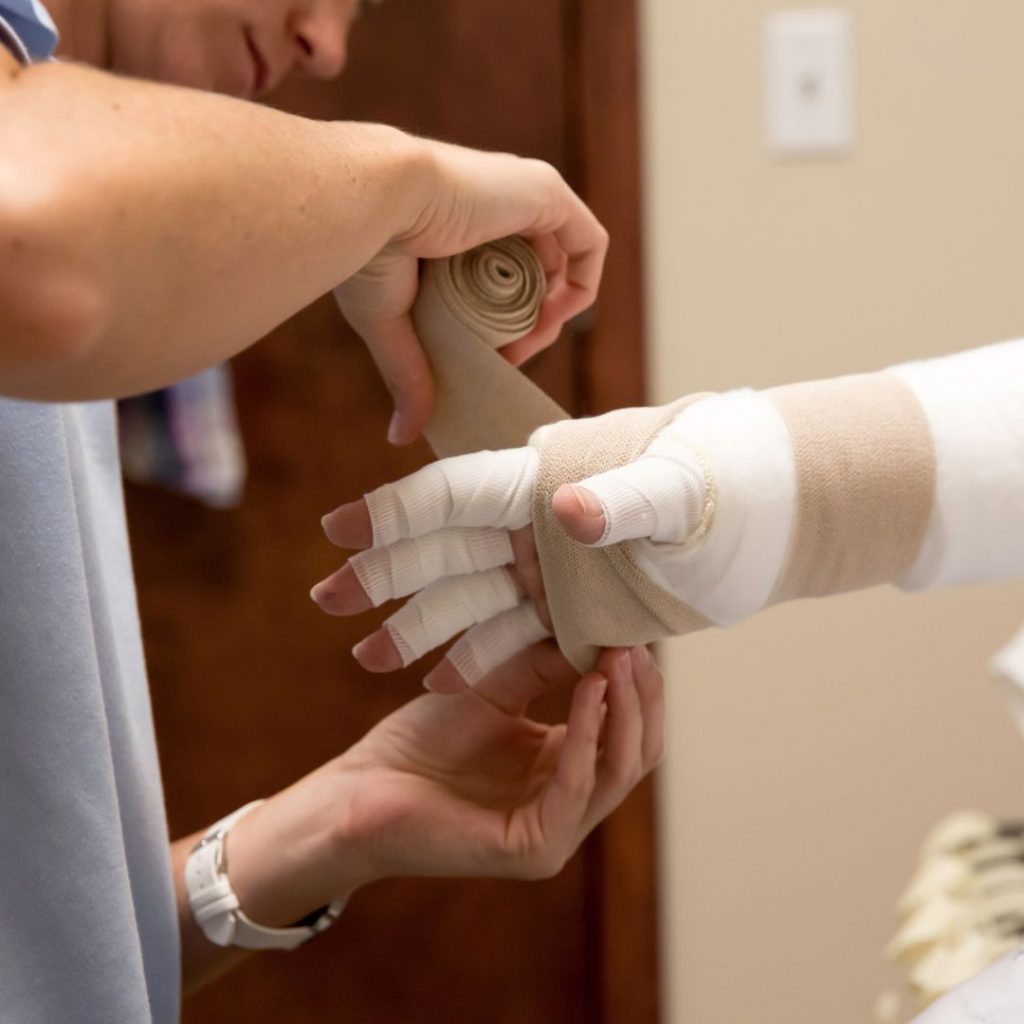
- Compression therapy involves using elastic bandages or unique compression sleeves and stockings to help reduce swelling and encourage lymph flow.
- Manual lymphatic drainage – a special massage that helps move the accumulated lymph fluid toward healthy lymphatic vessels, thereby reducing swelling.
- Exercise and physiotherapy – gentle, controlled exercises improve circulation and prevent further fluid accumulation.
- Skincare: Individuals with lymphedema must pay special attention to hygiene and skin hydration to prevent infections, which can further worsen the condition.
- Surgical interventions—In severe cases, when conservative methods do not yield results, surgery may be performed to improve lymphatic fluid flow.
Timely recognition of symptoms and the early initiation of therapy are crucial for preventing deterioration and preserving the functionality of the affected body part.
World Lymphedema Day – The Importance of Raising Awareness
Every year, World Lymphedema Day is observed to increase awareness of this condition and provide support to those affected. The goal of this day is public education, encouraging research, and improving access to treatment. Numerous organizations and associations worldwide organize events, campaigns, and lectures to raise awareness of the importance of early recognition and proper management of this condition.
Lymphedema is not only a physical burden but also an emotional and social strain for those affected. Many people face misunderstanding from those around them, lack of information, and difficulty accessing proper treatment. Raising awareness about this condition can help reduce stigma, foster a better understanding of the problem, and ensure a better quality of life for all those living with lymphedema.
Although lymphedema can be challenging, individuals can lead a fulfilling and active life with proper care, therapy, and support.